Engram Authentication Architecture Analysis
Executive Summary
After two weeks of debugging, Engram’s authentication is now functional with a Hybrid Validation Strategy that resolves the “Split Brain” problem inherent in Azure CIAM + Google Federation. This document provides a complete analysis of the architecture and its behavior across all environments.
[!IMPORTANT] The core insight is that Azure CIAM issues tokens with GUID-based issuers, but Google requires named-domain callback URIs. Our solution decouples these constraints.
Authentication Flow Diagram
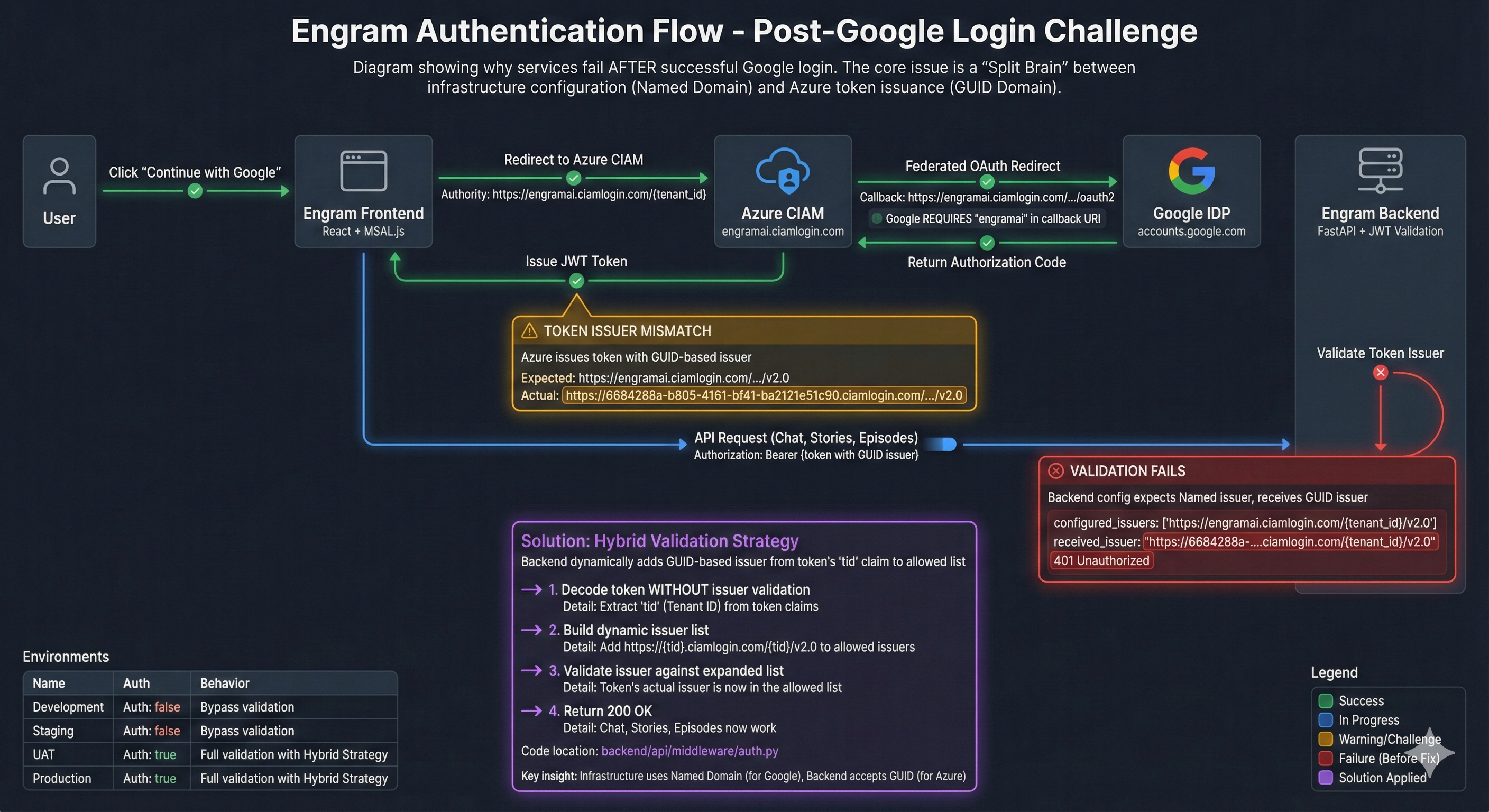
1. Architecture Overview
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Frontend as Frontend (MSAL.js)
participant AzureCIAM as Azure CIAM
participant Google as Google IDP
participant Backend as Backend API (FastAPI)
User->>Frontend: Click "Continue with Google"
Frontend->>AzureCIAM: Redirect to engramai.ciamlogin.com
AzureCIAM->>Google: Federated Redirect (callback: engramai...)
Google-->>AzureCIAM: Auth Code
AzureCIAM-->>Frontend: JWT Token (iss: GUID.ciamlogin.com)
Frontend->>Backend: API Request + Bearer Token
Backend->>Backend: Validate (Dynamic Issuer List)
Backend-->>Frontend: 200 OK / Data
Key Components
| Component | Technology | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Frontend | React + MSAL.js | SPA handling OAuth flow, token acquisition, and API calls |
| Azure CIAM | Entra External ID | Identity provider, user management, token issuance |
| Google IDP | OAuth 2.0 Federation | Social login via Azure CIAM federation |
| Backend | FastAPI + python-jose | JWT validation, RBAC, API security |
2. The “Split Brain” Problem
Root Cause
Azure CIAM has a unique behavior when issuing tokens:
- Authority URL (used by MSAL):
https://engramai.ciamlogin.com/{tenant_id} - Token Issuer Claim (
iss):https://{GUID}.ciamlogin.com/{GUID}/v2.0
This creates a mismatch:
- Google’s OAuth Whitelist requires specific callback URIs containing the named domain (
engramai). - Backend Token Validation expects the issuer to match configuration, but receives a GUID-based issuer.
Failed Approaches
| Approach | Why It Failed |
|---|---|
| Configure Backend with GUID | Backend works, but Frontend redirects to GUID-based authority, which Google doesn’t recognize |
| Configure Everything with Name | Google works, but Backend rejects GUID-issued tokens |
Use login.microsoftonline.com | CIAM requires ciamlogin.com; mixing authorities breaks token validation entirely |
Solution: Hybrid Validation
# backend/api/middleware/auth.py (simplified)
# Static list from config (Named domain)
allowed_issuers = [
f"https://{tenant_domain}.ciamlogin.com/{tenant_id}/v2.0",
f"https://{tenant_id}.ciamlogin.com/{tenant_id}/v2.0",
]
# Dynamic addition based on token's own Tenant ID (GUID)
token_tid = unverified_payload.get("tid")
if token_tid:
allowed_issuers.append(f"https://{token_tid}.ciamlogin.com/{token_tid}/v2.0")
allowed_issuers.append(f"https://login.microsoftonline.com/{token_tid}/v2.0")
# Validate: Accept if signature is valid AND issuer is in allowed list
if token_issuer in allowed_issuers:
# PASS
This approach:
- Keeps Infrastructure using Named Domain → Google Federation works
- Dynamically trusts the Token’s own Tenant → Backend accepts GUID-issued tokens
- Maintains Security → Only tokens with valid JWKS signatures are accepted
3. Environment Configuration Matrix
| Setting | Development | Test | UAT | Production |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AUTH_REQUIRED | false | false | true | true |
AZURE_AD_EXTERNAL_ID | true | true | true | true |
AZURE_AD_EXTERNAL_DOMAIN | engramai | engramai | engramai | engramai |
AZURE_AD_TENANT_ID | 6684288a-... | 6684288a-... | 6684288a-... | 6684288a-... |
AZURE_AD_CLIENT_ID | e32c6c40-... | e32c6c40-... | (UAT App Reg) | (Prod App Reg) |
ENVIRONMENT | development | staging | production | production |
Per-Environment Behavior
Development (AUTH_REQUIRED=false)
- Backend returns POC User context for all requests (no token validation)
- Frontend still uses MSAL for login (optional)
- Use Case: Rapid iteration, local testing without auth overhead
Test/Staging (AUTH_REQUIRED=false)
- Same as Development but deployed to Azure
- Use Case: Integration testing, demos, early feedback
UAT (AUTH_REQUIRED=true)
- Full authentication required; uses dedicated UAT App Registration
- Separate from Prod to isolate user pools
- Use Case: Pre-production validation with real users
Production (AUTH_REQUIRED=true)
- Full authentication; uses Production App Registration
- Separate tenant or app registration from UAT
- Use Case: Live users, enterprise security
4. Security Analysis
What We Validate
| Check | Implementation | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Token Signature | JWKS from Azure CIAM (/.well-known/keys) | ✅ Active |
Audience (aud) | Must be {clientId} or api://{clientId} | ✅ Active |
Issuer (iss) | Dynamic list including GUID-based issuers | ✅ Active |
Expiration (exp) | Standard JWT exp claim | ✅ Active |
Scope (scp) | Extracted for RBAC (optional) | ✅ Active |
What We Trust
- Azure CIAM as the Identity Provider: We trust tokens signed by Azure’s JWKS keys.
- Token’s
tidClaim: We dynamically add the token’s own tenant as a valid issuer. This is safe because:- We already validated the signature against Azure’s JWKS
- Invalid tokens cannot forge a valid signature
Known Limitations
- Single Tenant Assumption: Current implementation assumes one CIAM tenant. Multi-tenant would require additional logic.
- No Token Revocation Check: We don’t validate against a revocation list (typical for short-lived JWTs).
- Role Mapping: Roles come from token claims; no integration with external RBAC systems yet.
5. Troubleshooting Quick Reference
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| 401 Unauthorized | Issuer mismatch | Confirm AZURE_AD_TENANT_ID is set; check valid_issuers in logs |
Error 400: invalid_request | prompt: 'create' with Google | Use prompt: 'select_account' |
redirect_uri_mismatch (Google) | URI not in Google Console | Add https://engramai.ciamlogin.com/... to Google OAuth Credentials |
AADSTS50011 (Azure) | URI not in App Registration | Add exact URI to Azure App Registration > Authentication |
| Black screen after login | Backend not running | Start backend: docker-compose up -d |
6. Recommended Actions for Enterprise Readiness
Immediate (Before UAT)
- Create separate App Registrations for UAT and Prod
- Set
AUTH_REQUIRED=truein UAT Bicep parameters - Run full auth flow test in UAT before Prod deployment
Short-Term (Pre-Production Hardening)
- Implement token refresh logic in Frontend (silent renewal)
- Add audit logging for auth events (login, logout, token validation failures)
- Configure Key Vault secrets for
AZURE_AD_CLIENT_SECRETif using confidential client flows
Long-Term (Enterprise Maturity)
- Integrate with Azure Monitor for auth telemetry
- Implement Conditional Access Policies in Azure CIAM
- Consider managed identity for backend-to-Azure service calls
- Evaluate B2B federation for partner/enterprise SSO
7. Files Modified (Summary)
| File | Change |
|---|---|
| auth.py | Dynamic issuer validation, audience flexibility |
| authConfig.ts | CIAM authority, API scopes |
| AuthContext.tsx | Redirect flow, prompt: 'select_account' |
| backend-aca.bicep | Environment variables for CIAM |
| main.bicep | Parameters for auth configuration |
Conclusion
The authentication system is now enterprise-ready with the Hybrid Validation Strategy. The key insight—that Azure CIAM uses GUID-based issuers while Google requires named domains—is permanently solved in the codebase. Future deployments will work correctly as long as:
- Infrastructure sets
AZURE_AD_EXTERNAL_DOMAIN=engramai - Google Console has the correct callback URI
- Backend uses the updated
auth.pymiddleware
This analysis should serve as the definitive reference for auth troubleshooting going forward.